Content

Like assets, liabilities are split into current and long-term categories. Current liabilities have due dates within the next year, and long-term liabilities are due farther in the future. The accounting equation defines a company’s total assets as the sum of its liabilities and shareholders’ equity. Although most of the information on a company’s income tax return comes from the income statement, there often is a difference between pretax income and taxable income.
Actually, I think so too, but, how many assets/properties does he have ownership of?
I do believe he may own quite a bit of assets while having paper losses.
It’s a matter of balance sheet vs income statement.
— abandoned account (@Coolmott) September 28, 2020
Accounts on the income statement are either revenue or expense accounts. Creditors and investors often turn to these statements to assess your business’s growth, profitability, and value. There are five types of accounts in the general ledger found in your accounting software, and they’re found on either the balance sheet or the income statement. The income statement shows you how profitable your business is over a given time period. And the balance sheet gives you a snapshot of your assets and liabilities. Usually, investors and lenders pay close attention to the operating section of the income statement to indicate whether or not a company is generating a profit or loss for the period. Not only does it provide valuable information, but it also shows the efficiency of the company’s management and its performance compared to industry peers.
Both Involve A Companys Finances, But Their Differences Are Significant
Using a balance sheet and income statement to detail where your money is coming in and going out will be your guide in either continuing what you’re doing or look for ways to improve. The revenues section of this equation includes the money you’ve earned from customers. Your expenses section will include the costs your small business takes on to create products for customers. Your balance sheet will start off by listing your small business’s current and fixed assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. Both profit and loss statements and balance sheets are important for running your small business or corporation. Learn about these two different statements and about how they help your company’s future. The balance sheet and income statements complement one another in painting a clear picture of a company’s financial position and prospects, so they have similarities.
- Notice that we’ve shaded the accounts in the Chart of Accounts that are reported on the Income Statement – one income account and two expense accounts.
- Financial performance measures how well a firm uses assets from operations and generates revenues.
- This leftover money belongs to the shareholders, or the owners, of the company.
- While there’s no overlap in balance sheet and income statement accounts, net income appears on the balance sheet as part of retained earnings, an equity account.
- This is because you want your small business’s inception to be reflected on your balance sheet equity.
- The purpose of a balance sheet is to show your company’s net worth at a given time and to give interested parties an insight into the company’s financial position.
- Now let’s compare the P&L to budget to really see what’s going on with this business.
Look at them as a package because each one helps fill in the other’s blind spots. Add in the cash flow statement and you’ll have a full picture of your business’s financial health. The balance sheet and income statement highlight different aspects of your business’s financial history. It’s important to note that the trial balance is different from the balance sheet. This is an internal report that stays in the accounting department. The balance sheet, on the other hand, is a financial statement distributed to other departments, investors, and lenders. Items that create temporary differences due to the recording requirements of GAAP include rent or other revenue collected in advance, estimated expenses, and deferred tax liabilities and assets.
Using Balance Sheet Data
While these statements provide different insights, they are both used by investors and lenders to make decisions about your business. Once those factors are accounted for, you’ll have your net profit before taxes, also known as pretax income. Read the income statement from top to bottom, the line items are placed in logical order. Equity, calculated as the residual interest in the assets of an entity after deducting liabilities. The inventory will show up on your balance sheet as cash that has already been spent.


It’s often used as a report card of your company’s value to help attract investors. Preparing balance sheets can help to attract investors and paint a clear picture of your small business financials. Along with other financial information, balance sheet data is frequently analyzed and put into perspective through the construction of business and financial ratios. In many cases, ratios are constructed for each balance sheet for a number of years, so that you can make comparisons and spot important trends. Periodically prepared balance sheets are the primary financial tool for assessing the relative wealth or financial condition at a given point in time. Learn what to monitor and track to ensure your business is growing.
Two Reports, One Bucket
Construction Management This guide will help you find some of the best construction software platforms out there, and provide everything you need to know about which solutions are best suited for your business. The next financial statement, the balance sheet, helps tie together what the retained earnings mean to the overall value of the company. From an accounting standpoint, revenues and expenses are listed on the P&L statement when they are incurred, not when the money flows in or out. One beneficial aspect of the P&L statement in particular is that it uses operating and nonoperating revenues and expenses, as defined by the Internal Revenue Service and GAAP. An operating expense is an expense that a business regularly incurs such as payroll, rent, and non-capitalized equipment. A non-operating expense is unrelated to the main business operations such as depreciation or interest charges. Similarly, operating revenue is revenue generated from primary business activities while non-operating revenue is revenue not relating to core business activities.
Mind Your Farm Business — Ep. 69: BMPs for keeping up-to-date financial records – RealAgriculture
Mind Your Farm Business — Ep. 69: BMPs for keeping up-to-date financial records.
Posted: Thu, 09 Dec 2021 17:25:21 GMT [source]
The costs directly attributable to the production of the goods that are sold in the firm or organization are referred to as the cost of sales. Often, the individual balance sheet items can be improved to give a better-looking overall picture. For instance, you can improve cash balances by retaining cash collected on receivables until after the balance sheet date, rather than promptly spending the money. Enabling tax and accounting professionals and businesses of all sizes drive productivity, navigate change, and deliver better outcomes. With workflows optimized by technology and guided by deep domain expertise, we help organizations grow, manage, and protect their businesses and their client’s businesses. Gain perspective on a company’s financial well-being by learning to read its balance sheet.
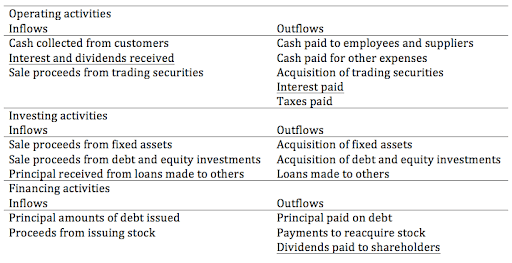
Operating Activities
Will showcase how your company is performing in terms of profit and loss. They will also show how quickly you can handle a financial disaster through your liquid assets. The income statement shows whether a company is generating a profit. Consequently, it can help managers identify problems reducing profits and opportunities for increasing profits.
What makes a strong balance sheet?
A balance sheet has three components – assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity. A strong balance sheet indicates a company is liquid, which means it has enough cash on hand to handle its liabilities. Having a large amount of cash is not the only determining factor when deciding whether a balance sheet is strong.
There’s a wealth of information there, some simply offering more detail than the line items of the balance sheet can provide—like accounting methods—or correcting errors in previous statements. Marking to market is a method of depreciation that does recognize this. It computes depreciated value based on what assets are worth on the open market. This means the depreciated value can go up or down over time. Originally developed to reflect changing values of futures contracts on a daily basis, marking to market aims to show the real-world value of a company’s assets and liabilities.
Company
In this way, the income statement and balance sheet are closely related. Balance sheets will show a more thorough overview of the security and investment health of a business, however they are both indispensable financial statements. Your balance sheet will be separated into two main sections, cash and cash equivalent assets on the one side, and liabilities and equity on the other. Documenting the financial details of your business will give you a thorough understanding of available cash flows so that you can make informed decisions about the viable future of your business. An income statement and a balance sheet will tell me the same thing, right? You’re looking at a multi-step income statement when you see gross profit, which is the difference between sales and cost of goods sold.



It is shown as a part of the owner’s equity in the liability side of the company’s balance sheet. Liabilities –Liabilities are obligations owned to others as of the balance sheet date. They arise from present obligations of a particular entity to transfer assets or provide services to other entities in the future as a result of past transactions or events. For purposes of the balance sheet, assets will equal the sum of your current and non-current assets — less the depreciation of those assets.
See For Yourself How Easy Our Accounting Software Is To Use!
If the company reports profits worth $10,000 during a period, and there are no drawings or dividends, that amount is added to the shareholder’s equity in the balance sheet. The income statement and balance sheet follow the same accounting cycle, with the balance sheet created right after the income statement.
What does a balance sheet represent?
A balance sheet is a summary of all of your business assets (what the business owns) and liabilities (what the business owes). At any particular moment, it shows you how much money you would have left over if you sold all your assets and paid off all your debts (i.e. it also shows ‘owner’s equity’).
ScaleFactor is on a mission to remove the barriers to financial clarity that every business owner faces. Equity is the amount of money originally invested in the company, as well as retained earnings minus any distributions made to owners. While it is relatively easy for an auditor to detect error, part of the difficulty in determining whether an error was intentional or accidental lies in the accepted recognition that calculations are estimates. It is therefore possible for legitimate business practices to develop into unacceptable financial reporting. Other expenses or losses – expenses or losses not related to primary business operations, (e.g., foreign exchange loss). Names and usage of different accounts in the income statement depend on the type of organization, industry practices and the requirements of different jurisdictions.
Shareholders’ equity is the sum of total assets minus total liabilities and is helpful in calculating a company’sfinancial health. Shareholders’ equity represents the net value or net worth of a company, which for Apple was $134 billion. This is the money left over for shareholders, assuming the company was to pay off all liabilities in the event of liquidation.
The income statement is a good entry point to understand and evaluate a company’s revenue and costs, but it’s important to keep in mind that it’s not a document that can tell the full story. “Financial statements are designed to work as a system and not as stand-alone statements,” adds Badolato.
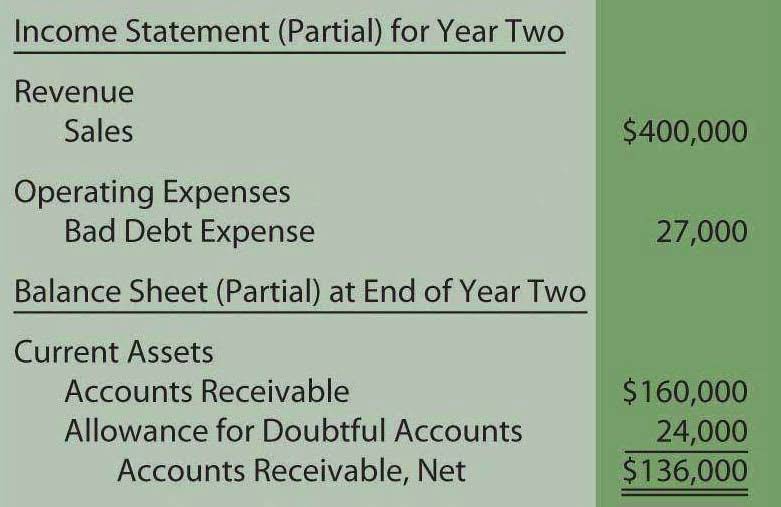


A company adopts strategies to reduce costs or raise income to improve its bottom line. The last component of the balance sheet is owner’s equity, sometimes referred to as net worth. The financial statement should balance, showing assets equaling liabilities plus owner’s equity. “The best way for investors to know how balance sheet example you’re going to treat their money is how you treat your money,” says Emily Chase Smith, Esq., author of The Financially Savvy Entrepreneur. The income statement shows information during a set period of time. On the other hand, the balance sheet shows the company’s financial position during a specific point in time.
Conversely, if costs are rising this can also be seen on the income statement and may lead an investor to ask more questions about the long term profitability of the company. Investors and financial analysts also use the income statement to derive popular financial ratios like Earnings Per Share . Give your statement a final QA either manually or using an automated platform. Using software allows you to automatically track and organize your business’s accounting data so you can easily access and review income statements.
Timing The balance sheet reveals the status of an organization’s financial situation as of a specific point in time, while an income statement reveals the results for a period of time. Compare the current reporting period with previous ones using a percent change analysis. Calculating financial ratios and trends can help you identify potential financial problems that may not be obvious. Managers use a balance sheet to determine if they can take on more debt for expansion, among other decisions. Looking at balance sheets for two different points can show whether the firm’s financial position has improved. For example, you can look at a company at the end of one year and the end of the previous year. Meanwhile, people often compare a company’s balance sheet to others in the same business.
Balance Sheet Vs Income Statement https://t.co/uLhx9iy4S6
— She NJW (@NjwMedia) December 6, 2021
This process of spreading these costs is called depreciation or amortization. The “charge” for using these assets during the period is a fraction of the original cost of the assets. A balance sheet provides detailed information about a company’s assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity. The balance sheet is one of the three fundamental financial statements. The financial statements are key to both financial modeling and accounting. Consolidated financial statements, such as a consolidated balance sheet, can also be useful when dealing with a parent company’s financial health and its subsidiaries. Like assets, they are categorized as either current or long-term.

